| Feature | Firewall 🔥 | Intrusion Detection System (IDS) 👀 | Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) 🚧 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Controls and filters network traffic | Monitors and detects suspicious activity | Detects and blocks threats in real time |
| Function | Enforces security policies (allow/block traffic) | Detects attacks but does not block them | Detects and blocks threats automatically |
| Placement | At the network perimeter or between zones | Inside the network (passive monitoring) | Inside the network (active protection) |
| Traffic Handling | Routes or drops packets based on rules | Sniffs traffic but does not modify it | Inspects and can drop malicious packets |
| Action Taken | Blocks/Allows based on source, destination, ports | Generates alerts/logs for potential attacks | Blocks/Drops packets in real-time |
| Performance Impact | Low (stateless) to Medium (stateful) | Low impact (just monitoring) | Higher impact (inline processing) |
| Type of Protection | Protects against unauthorized access | Detects attacks (e.g., DDoS, malware, exploits) | Prevents attacks before they reach target |
| Common Protocols Used | Packet filtering, stateful inspection | Signature-based, anomaly-based detection | Signature-based, behavioral analysis |
| Example Devices | Cisco ASA, Palo Alto, FortiGate, pfSense | Snort (IDS mode), Suricata (IDS mode) | Snort (IPS mode), Suricata (IPS mode) |
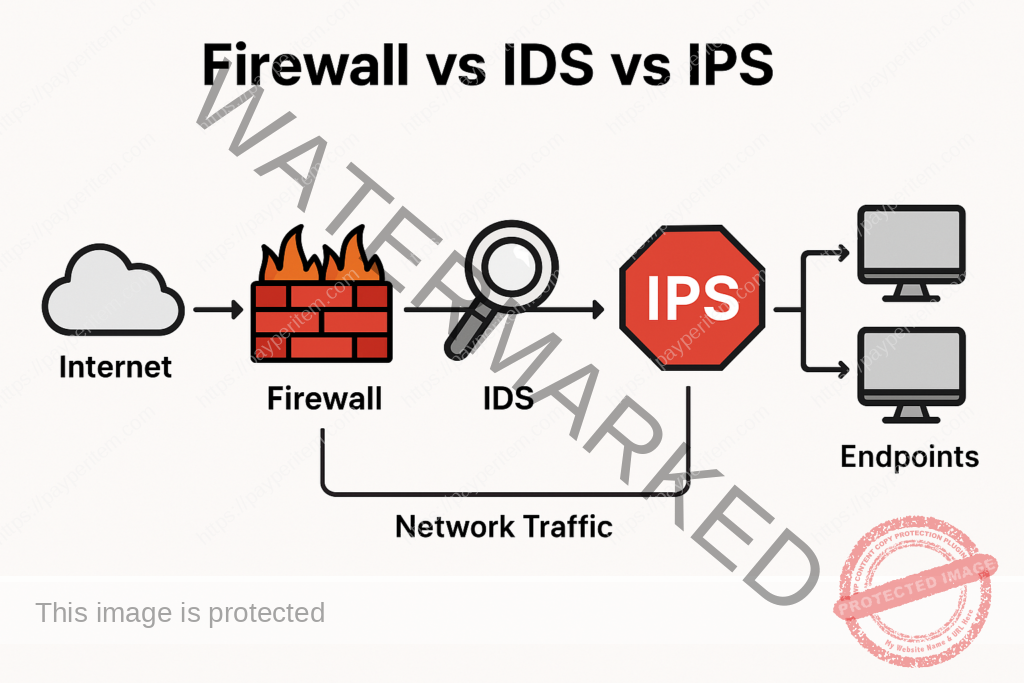
🖼️ Diagram: Firewall vs IDS vs IPS Architecture
Here’s how they fit into a typical network:
1️⃣ Firewall: Controls traffic at the network boundary
2️⃣ IDS: Monitors network traffic for threats (passive)
3️⃣ IPS: Actively blocks malicious traffic before it reaches endpoints